3.4 Grafting & Pre-Prosthetic Surgery
Grafting & pre-prosthetic surgery corrects abnormalities prior to prosthetic insertion (e.g. dentures and implants). Grafting, and specifically post-extraction ridge maintenance acts as a scaffold to help the body regenerate new bone.
Types of Grafts:
- Allograft: bone from another human donor
- Autograft: bone from the patient’s body
- Autogenous: tissue from the patient’s body
- Xenogenous: tissue from another animal species (bovine, equine, porcine)
- Xenograft: bone from another animal species (bovine, equine, porcine)
- Xeno-synthetic: grafts made from man-made materials (hydroxyapatite and polymers)
Categories:
Aseptic Technique is required –
- Soft tissue: removal or repair of fibrous, hyperplastic, and hypertrophic tissue.
- Alveolar ridge maintenance immediately following extraction: Allograft.
- Tori Removal: Maxillary palatal tori and mandibular lingual tori are removed prior to denture insertion.
Sterile Technique is required –
- Block bone grafts: Autograft of a large area. The donor bone is intact and held in by bone screws.
- Bone grafts: Autograft. The donor bone is placed into the surgical site.
- Sinus lift: with allograft or autograft, osteotome or elevation.
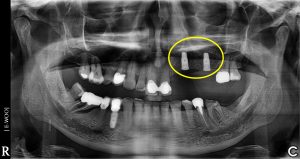
Note the sinus elevation in preparation for maxillary left implants 
Sinus lift pan
IMPORTANT: Various sites are used for autografts, such as: the ramus of the mandible, and the chin area (block grafts bone scraping, or milling). The maxillary tuberosity is also an area where softer bone can be harvested. Bone can also be collected while performing the osteotomy during implant placement. In all cases, autograft must be placed in a sterile bowl with sterle saline until the recipient site is prepared.
Membranes provide a barrier between residual bone or grafted bone and the soft tissues to prevent the tissue cells from populating the bony defect and preventing regeneration of bone.
Types of Membranes:
- Platelet Rich Fibrin (PRF) membranes: Autogenous – PRF Protocol

The centrifuge and PRF pan 
PRF tray 
The blood after it’s been spun in the centrifuge (note: the PRF is the top layer) 
PRF membranes - Collagen Membranes: Xenogenous
Post-operative Considerations:
REMEMBER: All grafting materials must be recorded for recall purposes. This can be done online AND a backup copy is recommended. Each material comes with a discrete Lot and Reference number on stickers that must be placed in the patient’s chart and a practice wide filing system (sorted by date).
An excellent resource:
Bone Grafts in Dentistry
