Unit Three – OMS Procedures
Learning Outcomes
Explain common OMS procedures and select the dedicated armamentarium for each procedure
Goal
Assist in common OMS procedures as an integral part of the surgical team
Common Procedures
Extractions – the removal of teeth
- single or multiple teeth
- 4×8 – extraction of 4 third molars (wisdom teeth)
Orthodontic Interventions – surgeries designed to assist in orthodontic treatment (correction of malocclusions)
- Bollard Plates – titanium plates that are temporarily screwed into the jaw; they provide anchorage for orthodontic movement
- Exposures – surgical uncovering of a tooth in preparation for orthodontic treatment
- Frenectomy – removal of tissue that prevents the normal position of teeth, tongue, (or prosthetic)
- Luxate – surgical dislocation or displacement of a tooth from the alveolus to assist in eruption
- Transplant – surgical removal of a tooth from one location to another
Biopsy – removal and examination of abnormal oral structures
- Cysts and periapical lesions
- Soft tissue lesions
Pre-Prosthetic Surgery – corrects abnormalities prior to prosthetic insertion (e.g. dentures and implants)
- Soft tissue: removal or repair of fibrous, hyperplastic, and hypertrophic tissue
- Alveolar ridge maintenance post-extraction: Allograft
- Platelet Rich Fibrin (PRF) membrane: Autograft
- Collagen membranes: Allograft
- Block bone grafts from patient’s donor site: Autograft
- Bone grafts from patient’s donor site: Autograft
- Sinus lift: with allograft or autograft, osteotome, or elevation
- Tori Removal
Implantology – replacement of single tooth, multiple teeth, or full arches
- First stage (initial placement): single, multiple, all-on four (full arch)
- Second stage (typically 3-4 months post placement): assess for osseointegration, ISQ test, uncover
Orthognathic Surgery – corrects conditions of the jaw related to structure, growth, malocclusion or trauma
- BSSO – Bilateral Sagital Split Osteotomy
- Genioplasty – chin augmentation
- Le Fort 1 – Maxillary Osteotomy
- SARPE – Surgically Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion
TMJ Surgery –
- Arthrocentesis – TMJ arthrocentesis is a surgical treatment that involves irrigating the joint with the possibility of depositing a therapeutic drug
- Eminectomy – A surgical reduction of the articular eminence of the TMJ
Emergency Surgery – emergent maintenance of circulation issues, pain, and infection
- Cautery – coagulation of tissue by an electric surgical device
- Debridement – removal of damaged tissue or foreign object from a wound
- Facial Trauma – jaw wire
- Incise and Drain (I & D) – clinical lancing
- Oral-Antral Fistula – sinus exposure
It is always best to confer with your surgeon when choosing procedure specific protocols to prevent healthcare associated infections. Below are some examples:
PROCEDURE SPECIFIC PROTOCOLS:

Planning reduces errors in OMS. Creating procedure specific checklists will ensure the utmost in perioperative care, and in maintaining asepsis or sterility
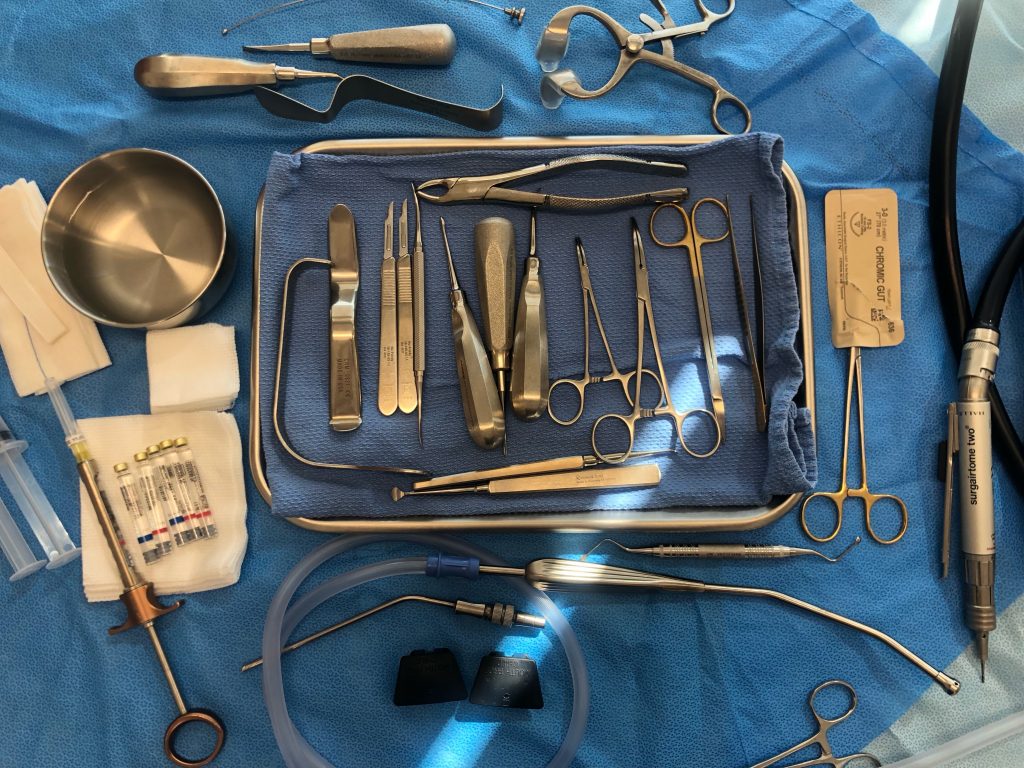
Surgical Tray:
The tray sets pictured are generic and are used for all procedures
Specialized equipment and instruments are picked for each procedure
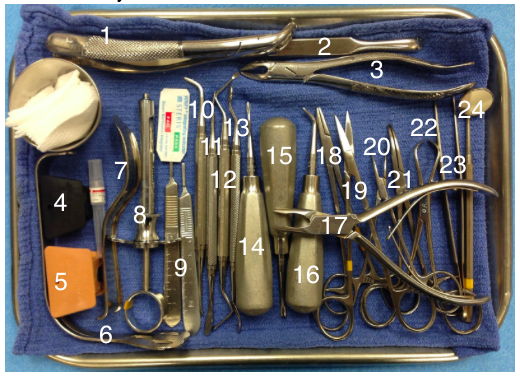
| 1 Lower Universal Forcep | 13 Bone File |
| 2. Seldane Retractor | 14 #301 Straight Elevator |
| 3.Upper Universal Forcep | 15 Coupland Elevator |
| 4 Small Mouth Prop | 16 Crane Elevator |
| 5 Large Mouth Prop | 17 Rongeur |
| 6 Tongue Retractor | 18 Suture Needle Driver |
| 7 Minnesota Retractor | 19 Scissors |
| 8 Local Anesthetic Syringe | 20 Mosquito Hemostat |
| 9 Scalpel Blade Handles | 21 Hemostat |
| 10 #12 Periosteal Elevator | 22 Towel Clamp |
| 11 #9 Periosteal Elevator | 23 Tissue Forceps |
| 12 Currette | 24 Mouth Mirror |
Note: The sterile indicator tag on each tray (as seen above) is crucial to ensure sterility
Surgical Tray with Suction and Power: