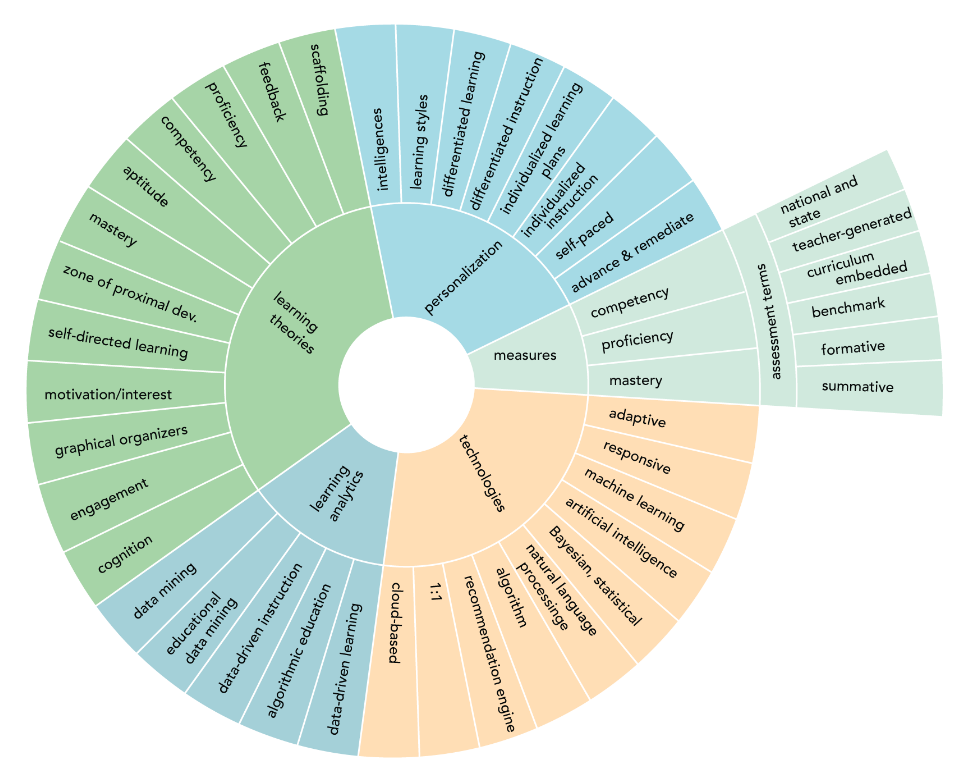
Additional Content
Other terms related to Personalised learning
Some types of learning and instruction, which are often used while discussing personalised learning:
Blended learning
This is a cohesive mix of face-to-face-instruction and online learning. The teacher could either produce content for online learning or use a content provider such as Kahn Academy. Blended learning often involves a learning management system such as Moodle or Google Classroom that integrates both parts and helps keep track of student learning1.
Competency-based learning
Content, skills and dispositions can all be described as competencies that a student has to acquire. In competency-based learning, once a student has demonstrated mastery of one competency, they move on to the next. When they have trouble, they are given help1,2.
This is an alternative to the traditional setting where progress is based on student’ age and time spent in the classroom.
Differentiated instruction
“To differentiate instruction is to recognise students’ varying background knowledge, readiness, language, preferences in learning and interests; and to react responsively”3. It is different from personalised learning in that it is not student-led and the learning objective is common to all learners – the only change is in the method of instruction.
For example, for learning new words, some students may be asked to find newspaper clippings that feature these words; others might be asked to learn a song.
Flipped classroom
This flips the classwork and homework. Students learn at home using online coursework or lectures. The teacher guides practice or projects when in the class2.
Individualized learning
This is all about the pace in which a student learns4. If they are struggling, they can opt to spend more time practising what they learnt. If they are confident, they can move ahead and explore more content without getting bored.
Problem-based learning and project-based learning
Students learn by solving a problem or doing a project which may or may not be personalized, while teachers act as their facilitators or guides.
1 Groff, J., Personalized Learning: The State of the Field & Future Directions, Center for Curriculum Redesign, 2017.
2 Holmes, W., Anastopoulou S., Schaumburg, H & Mavrikis, M., Technology-enhanced personalised learning: untangling the evidence, Stuttgart: Robert Bosch Stiftung, 2018.
3 Hall, T., Vue, G., Strangman, N., & Meyer, A., Differentiated instruction and implications for UDL implementation, Wakefield, MA: National Center on Accessing the General Curriculum, 2003.
4 Michell, M., Personalized, Individualized, and Differentiated Learning: A Simple Math Equation, 2016.
