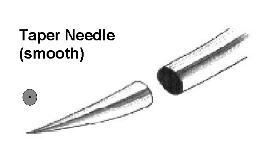
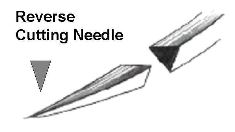
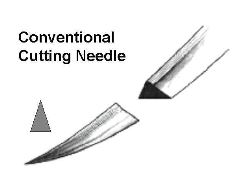
Suturing of Uncomplicated Lacerations
- Goggles
- Sterile gloves
- Laceration tray (sterile gauze, waterproof drape, tissue forcep, needle holder, sterile scissors)
- Sterile normal saline
- Chlorhexidine (or other approved skin cleanser)
- Anesthetic such as Xylocaine 1% and/or 2%
- 10mL syringe with a 25-gauge needle
- Suture material
- Dressing (such as Mepore)
ABSORBABLE |
NON-ABSORBABLE |
| • readily broken down in the body by enzymes or hydrolysis | • not readily broken down in the body |
| • made of synthetic or naturally occurring material | • made of synthetic or naturally occurring material |
| • use in subcutaneous tissue and when continued strength not required | • provides continued strength to healing tissue |
| Ex: Chromic, Vicryl, Monocryl | Ex: Silk, Prolene, Nylon |
SIZE |
USE |
| 3-0 | Scalp, torso, hands |
| 4-0*size most commonly used for superficial wound closure | Extremities |
| 5-0 | Face, nose, ears, eyebrows |