2 What Do Instructional Designers Do?
Author’s NoteThis chapter was originally published as a post on the Power Learning Solutions Blog (Power, 2019) on January 9, 2019. |
What is Instructional Design?
On the surface, this question sounds like it should have a straightforward answer. But, often, the definition of instructional design can be murky because there is much that it encompasses. Right now, I am facilitating some introductory-level instructional design courses at different Canadian universities. I thought that it might be helpful to draw upon some of their course resources to summarize what instructional design is from my perspective.
In one of my courses, participants are asked to review a blog post by Tom Kulhmann (2008). Kulhmann’s post What Everbody Ought to Know About Instructional Design provides a video example and discusses its instructional design elements. Along the way, he injects five key bullet points about what instructional design is:
- Instructional design is more than just putting information in front of learners.
- Instructional design has clear goals, and gets your learners focused on the right things.
- Instructional design provides context and perspective.
- Instructional design compresses the learning process and saves time.
- Instructional design engages learners with clear and meaningful content.
For the most part, I agree with Kulhmann’s observations — although I would argue that “compresses the learning process and saves time” is not always a desired objective of the ID process. That would all depend on the context — and in some contexts, you may want to deliberately extend the learning process! However, I think that there are enough “gems” in Kulhmann’s points to craft a basic working definition of instructional design for those “new to the game.”
“Instructional design is the process of establishing clear learning goals, and then creating a plan, environment, and resources, that engages learners with meaningful content and clear and purposeful activities” (Kulhmann (2008).
Yes, there is a lot more to instructional design than what this definition would imply! I’m deliberately keeping things succinct for the purposes of this chapter. But, perhaps a look at what instructional designers do might give a better sense of the scope of the field.
What is the Role of the Instructional Designer?
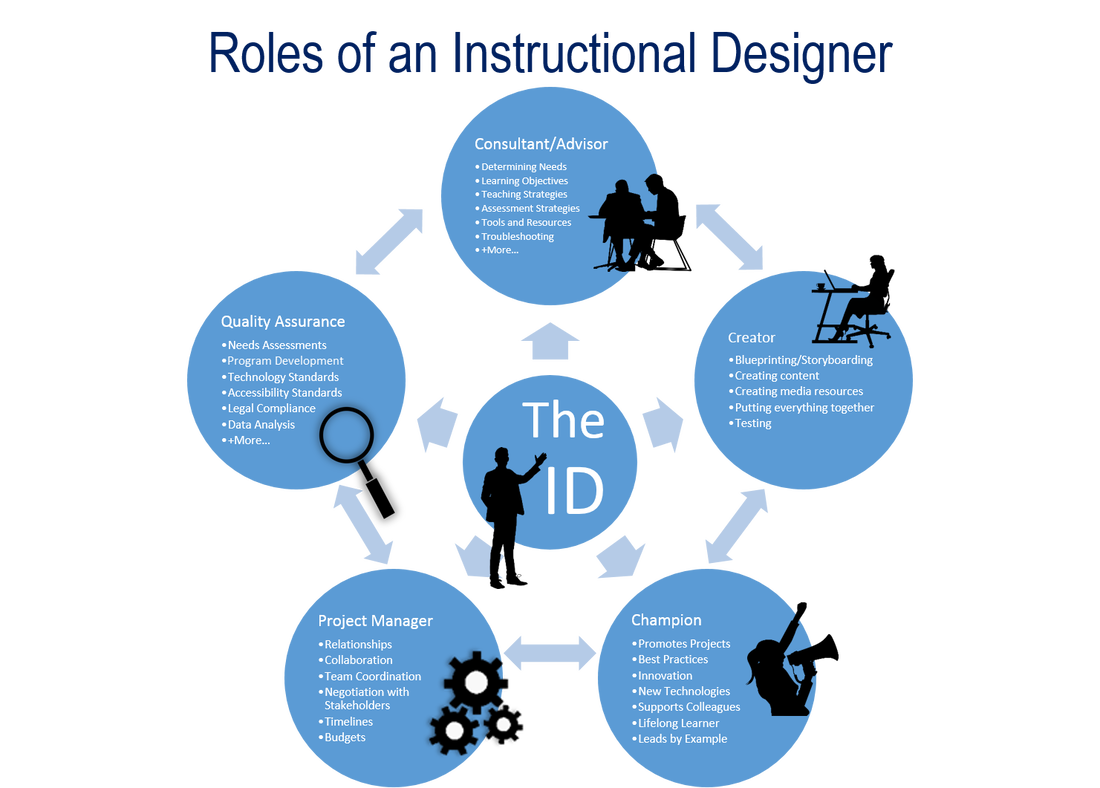
The precise roles and tasks of an instructional designer may vary, depending on their school or organization. I’ve created the following infographic to illustrate the breadth of the roles that I’ve played as an instructional designer and instructional developer. These roles include:
- Consultant / Advisor
- Creator
- Champion
- Project Manager
- Quality Assurance
And, of course, there is a lot of overlap between all of these roles!
Further Reading

Kenny, Zhang, Schier, and Campbell (2005)’s A Review of What Instructional Designers Do: Questions Answered and Questions Not Asked. This is a brief literature review published in 2005 that is a bit longer, but worth the read to get a sense of what instructional designers do.
Read the article What everyone ought to know about instructional design. This article is from the Rapid E-learning Blog by Tom Kulhmann (2008). It provides a good overall explanation of instructional design and its value and is a useful place to begin. It’s also fun! If you are interested you can subscribe to Tom’s blog.
Watch the video presentation “How Education Works” presented by Jon Dron at MADLaT 2014. In this presentation, Dr. Dron defines technology as objects, as knowledge, as activity and as a societal system. Technology and learning are inherently linked, and how we view both the role of technology and pedagogy is part and parcel of the confusion about instructional design. In some institutions the instructional designer is the person who knows computer programming or graphic design. It’s the person who can “help get my course online.”
Read the definitions of Instructional Design, Educational Technology and Instructional Technology from Instructional Design Central (2022).
Watch the video Reimagining Learning from Richard Culatta at TEDx Beacon Street (TEDx Talks, 2013):
References
Dron, J. (2014, April). How education works. [Video presentation]. MADLaT 2014. https://etv.academic.rrc.ca/Mediasite/Play/c2afd219b64349faa81ae8bf275ec93e1d
Instructional Design Central (2022). Instructional Design Definitions. https://www.instructionaldesigncentral.com/whatisinstructionaldesign
Kenny, R.F., Zhang Z., Schwier, R.A., & Campbell, K. (2005). A review of what instructional designers do: Questions answered and questions not asked. Canadian Journal of Learning and Technology, 31(1), 9 – 26. http://auspace.athabascau.ca/bitstream/2149/390/1/What Instructional Designers Do.pdf
Kulhmann, J. (2008, July 22). What Everybody Ought to Know About Instructional Design. Rapid eLearning. https://blogs.articulate.com/rapid-elearning/what-everybody-ought-to-know-about-instructional-design/
Power, R. (2019, January 9). What Do Instructional Designers Do? Power Learning Solutions. https://www.powerlearningsolutions.com/blog/what-do-instructional-designers-do
TEDx Talks (2013, June 10). Reimagining Learning from Richard Culatta at TEDx Beacon Street. https://youtu.be/Z0uAuonMXrg
