15.5 Special Topics in Logistics
After exploring the strategic and operational aspects of transportation and warehousing, it’s important to discuss a few additional topics that round out our understanding of logistics and its application in business.
15.5.1 Logistics Partners
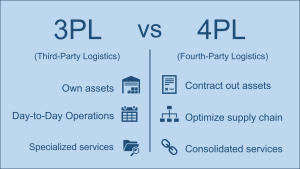
3PL (Third-Party Logistics): Logistics firms often specialize in specific types of services. For instance, one company might focus on last-mile transport, another on warehousing, and yet another on long-haul transport. These specialized service providers are known as third-party logistics providers, or 3PLs. Businesses typically need to coordinate with multiple 3PLs to manage their diverse logistics needs effectively. Most 3PLs own the assets they use to provide the service.
4PL (Fourth-Party Logistics): In contrast, 4PL firms offer consolidated logistics services, presenting businesses with a single-window solution for all their logistics requirements. Most 4PL providers do not own the assets and contract with 3PLs to furnish these services. While using a 4PL can be more convenient, it might also be more costly. Additionally, while businesses retain full control over their choice of logistics providers in a 3PL model, this control may be diluted with a 4PL, as these firms select service providers based on their criteria.
15.5.2 Technology in Logistics
 The logistics sector has witnessed significant technological advancements in recent years. While a detailed discussion on technology in supply chains is reserved for the next chapter, here are brief highlights of three key tools:
The logistics sector has witnessed significant technological advancements in recent years. While a detailed discussion on technology in supply chains is reserved for the next chapter, here are brief highlights of three key tools:
Load Boards: These are online matching systems where shippers and carriers can post and find loads for transport. Load boards help in optimizing the utilization of transportation resources, reducing empty runs, and facilitating quicker, more efficient shipping arrangements.
Transportation Management System (TMS): A TMS is a platform that aids businesses in planning, executing, and optimizing the physical movement of goods. It encompasses functionalities like carrier selection, freight auditing, and route planning, contributing to more efficient and cost-effective transportation processes.
Warehouse Management System (WMS): A WMS is specialized software designed to support and optimize warehouse functionality and distribution center management. This includes managing inventory levels, optimizing picking and packing processes, and streamlining warehouse operations.
15.5.3 On-Demand Warehousing
On-demand warehousing is a novel concept that offers flexible and scalable fulfillment options, akin to ride-sharing but in the realm of warehousing. This model utilizes a network of shared warehouse spaces and fulfillment services, allowing businesses to access necessary warehousing resources only when needed. This approach eliminates the requirement for long-term leases or investments in physical warehouse space, offering a versatile solution for businesses with fluctuating storage needs.
