3.5 Quality Assurance and Quality Control in SCM
Quality Assurance and Quality Control are two fundamental, yet distinct, components of a comprehensive quality management strategy to ensure the consistent delivery of high-quality products or services. They offer unique approaches to ensuring quality but work together to achieve the overall objective of delivering a high-quality product or service. Both play crucial roles in maintaining the desired level of quality in a supply chain, safeguarding the customer’s interests, and promoting efficiency and effectiveness.
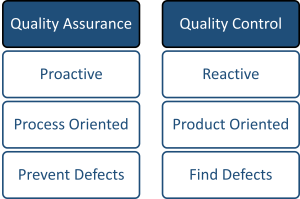
Quality Assurance (QA) is a proactive process that focuses on the process and prevents defects by ensuring the process is designed and controlled correctly. QA is about designing and implementing a system that ensures the product or service is produced under controlled conditions that lead to consistent quality. It is more process-oriented and geared towards preventing defects.
Quality Assurance in supply chain management is about developing and implementing a system that ensures all processes, from procurement of raw materials to production and delivery of the final product, meet the predefined quality standards. QA methods are used to improve the supply chain processes, minimize variability, reduce waste, and ensure that the final products meet the customer’s expectations.
Quality Control (QC), on the other hand, is a reactive process that is product-oriented and involves checking final products for defects. It involves inspecting and testing the actual products or services to identify and correct any defects that have occurred. QC is more product-oriented and aims at identifying defects in the finished products before they reach the customer.
Quality Control is important in detecting and correcting problems that occur during the production process. QC activities, such as inspection and testing, help ensure that the final product or service meets the defined quality standards. By identifying and correcting defects before the product reaches the customer, QC contributes to customer satisfaction and maintains the organization’s reputation.
In the context of supply chain management, both QA and QC are vital for maintaining and improving the quality of products or services.
Common Techniques Used in QA and QC
Several techniques are commonly employed in QA and QC, including:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): This involves using statistical methods to monitor and control a process to ensure that it operates at its full potential.
- Process Auditing and Reviewing: Regular audits and reviews of the supply chain processes can help identify areas of improvement and ensure that the processes comply with the quality standards.
- Inspections: Regular inspections of raw materials, components, and final products can help detect defects early and prevent poor quality products from reaching the customer.
- Testing: This involves evaluating the performance of a product under certain conditions to ensure it meets the quality standards.
Understanding the role of QA and QC in supply chain management and effectively employing them in the quality management system helps ensure consistent quality, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance the efficiency of the supply chain processes.
