PATIENT PREPARATION
Pre-Abortion Evaluation
- Most preparation is equivalent to evaluation for abortions ≥ 14 weeks, including
- systematic review of patient’s medical history, sexual / reproductive history, medications, substance use, and allergies is recommended (see Ch 3 Lab Tests if Indicated)
- Rh, H/H, STI tests as needed, glucose in IDDM (see Ch 3 Pre-Abortion Evaluation)
- Additional information for procedures ≥14 weeks includes:
-
Ultrasound with placental location for all patients ≥ 14 weeks
-
Ultrasound with doppler flow (by the person with most experience available) to screen for placenta accreta spectrum (PAS):
-
Anterior low-lying (<2 cm from internal os) or placenta previa + previous uterine surgery / scar
-
Tips: For initial placental location view uterine-bladder interface in sagittal plane. Fundal placentation is quite reassuring. For specific US and doppler findings of PAS see: (Adu-Bredu 2022)
-
Patients with a prior uterine surgery / scar may have a procedure in an outpatient setting, after appropriate evaluation to exclude PAS. (NAF CPG 2022)
-
For rare PAS, refer to a higher level of care to mitigate hemorrhage risk.
-
-
Pre-Abortion Procedures
Patients receiving abortion care at >14 weeks should receive:
- IV for ease of administration of medications and due to the increased risk of bleeding in later gestations, and greater likelihood of needing conscious sedation (NAF 2022)
- Routine antibiotic prophylaxis initiated at insertion of osmotic dilators or co-administered with pain medications prior to misoprostol cervical prep or procedure itself (NAF 2022). (See Ch 5 Pre-procedure medications)
- Appropriate pain management given likelihood patients >14 weeks will benefit from conscious sedation due to greater cervical dilation, procedure time and uterine instrumentation. (See Ch. 5 Pain Management)
Cervical Preparation
Adequate cervical ripening and dilation is necessary to allow for uterine evacuation, and minimize prolonged, difficult, or traumatic procedures (Grimes 1984, Schulz 1983). Approaches vary by region, training, available resources, staffing, flow, clinical history, and patient-centered wait time considerations. Cervical preparation initiated early in the day can facilitate same-day D&E procedures. These recommendations are suggestive rather than prescriptive, as many methods have been validated as safe and effective, with minimal difference in procedure time and complications. (Newmann 2010)
Table 1. Properties of various cervical ripening agents(Fox 2013, Paul et al (eds) 2009) |
|
| Misoprostol | Prostaglandin E1 analogue providing cervical ripening and dilation. Dose range 200-800 mcg (400 mcg most common) 30 min-4 hr prior to procedure. |
| Mifepristone | Progesterone receptor antagonist providing cervical ripening and increased misoprostol responsiveness;. Dose 200mg 24-48 hr prior to procedure.
Mild increased risk of pre-procedure pregnancy expulsion (Newmann 2010). |
| Synthetic osmotic dilator (Dilapan-S®) | Synthetic osmotic dilator with strong outward radial force with maximum dilation (3-4x original diameter) within 4-6 hours (so good option for same day cervical prep). Comes in 3-4mm D by 55-65mm L. May shorten as it swells which may impact internal os dilation if not adequate length. Expensive. |
| Laminaria | Sterilized seaweed rods with both radial force and some prostaglandin release properties at maximum dilation (3-4x original diameter without shortening) within 12-24 hours. Comes in a wide range of sizes 2-10mm D by 60-85mm L. Avoid for iodine and seafood allergies. |
| Foley balloon | Foley balloon placed within the cervix, inflated to 30-50mL of normal saline, and taped to the patient’s leg overnight. Maximum dilation of 1.5-4 cm. Alternative to osmotic dilators beyond 18 weeks (Sium 2022). |
Most procedures from 14-18 weeks can be accomplished via same-day cervical prep methods (see below). Same day misoprostol alone is usually adequate to achieve cervical ripening for dilation to 16-17 weeks (49 or 51 pratt). (Nucatola 2008, Fox 2013)
Greater same-day dilation can be achieved with the placement of one to several synthetic osmotic dilators (Dilapan-S®) in addition to misoprostol given vaginally or buccally. Osmotic dilators, when placed in the closed cervix, absorb moisture from the tissues and swell, opening the cervix with little discomfort. To minimize hourglassing and to aid in removal – consider placing a “keyhole” dilator in center of the set, extruding more from external os, OR using a combination of synthetic osmotic dilators (which stretch more with traction to remove) and laminaria (which undergo less radial expansion during same-day prep). (see Figure 9 and Tables 1 & 2 for specific types and considerations)
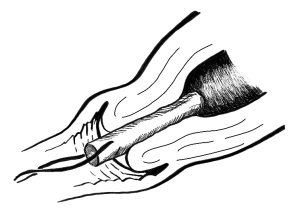
Figure 5. Correct osmotic dilator placement, through external and internal os, ensures uniform dilation
Although rarely needed for this EGA range, two-day procedures can be planned, using cervical preparation with mifepristone and/or osmotic dilator placement on day 1, followed by misoprostol on the procedure day.
Table 2. Options for cervical preparation approach(es)¹ |
||
| Gestational Age | Misoprostol |
Osmotic Dilators Synthetic (Dilapan-S®) & Laminaria |
| 12w0-15w6 | 400-600 mcg x 90 min | (Dilapan-S®) +/- lams x 4 hour |
| 16w0-16w6d² | 400-600 mcg x 90 min – 3 hour | (Dilapan-S®) +/- lams x 4 hour |
| 17w0-19w6² | 400-600 mcg x 4 hour | (Dilapan-S®) +/- lams x 4 hour or overnight lams or foley |
|
¹Some providers consider shorter wait times for history of prior vaginal delivery and no prior c-section. ²Some providers use a combination of same-day synthetic osmotic dilators with misoprostol, though no evidence for osmotic dilator #, or improved procedural outcomes for GA <18-19 wk (Ralph 2019). |
||
Deciding whether patients may leave the clinic area after administration of misoprostol and/or osmotic dilator placement will depend on each clinic and patient. Pain management, anxiolytics, and anti-emetics should be offered as needed for each patient. Consider allowing the patient to leave the clinic during cervical prep wait time if the patient is:
- comfortable and experiencing no more than scant bleeding
- has normal vital signs
- has no IV in place
- has not received opioids or benzodiazepines
- has no history of c-section or current placenta previa.