ULTRASOUND (US) OVERVIEW, METHODS, TIPS & IMAGES
US is not a requirement for medication abortion or uterine aspiration. US can be used when clinical dating is uncertain, to determine pregnancy location, viability, and / or provide procedural support.
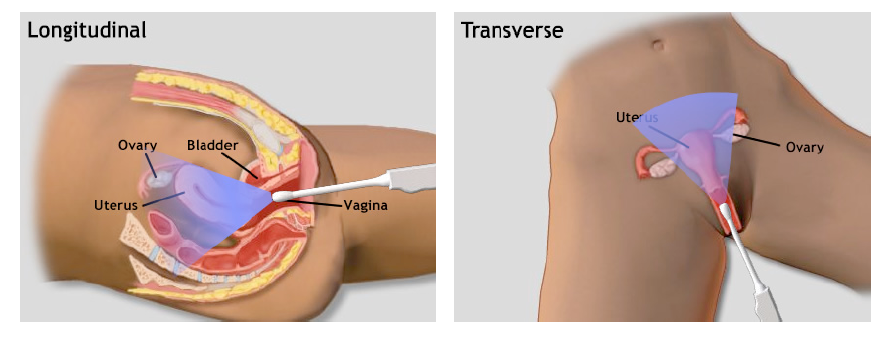
Whether to use transabdominal or transvaginal US depends on patient preference, equipment availability, gestational age, and sonographer skill. Transabdominal US may be used to confirm intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) and assess gestational age; it is often preferred by patients, although transvaginal US is often helpful with earlier pregnancies (Fu 2018).
| Transabdominal Probe | Transvaginal Probe |
|---|---|
|
|
A limited first trimester US exam must include: (NAF CPGs 2022)
- Uterine scan in both longitudinal and transverse planes to confirm IUP
- Evaluation of pregnancy number (singleton or multiple gestation)
- Measurements to document pregnancy dating
- Evaluation of pregnancy landmarks, such as yolk sac, embryonic pole, and the presence or absence of fetal/embryonic cardiac activity
When Performing US
- Ask if the patient wants to view the image, and be informed of multiple gestations or other pregnancy findings.
- Inform the patient that US is being used only to confirm the location and dating of the pregnancy and is not a diagnostic US.
- Consider starting your scan with transabdominal US, and switching to vaginal US only if you are unable to effectively visualize the pregnancy.
- For vaginal US, use a non-latex probe cover, with US gel inside and lubricating jelly outside. Ask if the patient would prefer to self-insert the probe.
- Systematically scan in the longitudinal and transverse planes.
- Use clear and simple language to discuss the US findings with the patient.
TVUS planes (Image ARMS 2007)
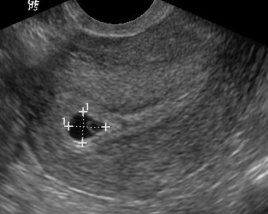
- Longitudinal view is used to confirm pregnancy is intrauterine. For longitudinal view, marking is up (12 o’clock) and uterus is scanned side to side, from ovary to ovary. This view should show uterine fundus connected to cervix with pregnancy inside the uterus.
 (Images AIUM Image Library: Obstetrics 2018)
(Images AIUM Image Library: Obstetrics 2018)
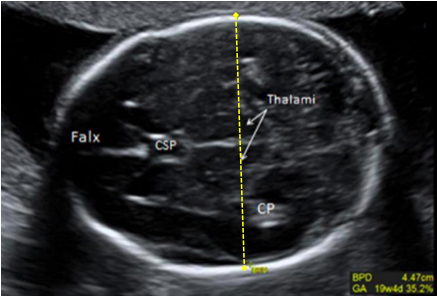
- Transverse view is used for dating and pregnancy landmarks, to evaluate for multiple gestations, and to obtain a full 3D image of the uterus. For transverse view, the probe is turned 90 degrees to the patient’s right (counterclockwise or notch turned to 9 o’clock) and uterus is scanned anterior to posterior, from fundus to cervix.
Clinicians should understand the sonographic pregnancy features that should be visible based on the patient’s last menstrual period.
| Pregnancy Landmarks by Weeks LMP | |
| Gestational Sac | 4.5 – 5 weeks LMP |
| Yolk Sac | 5.5 weeks LMP |
| Embryonic Pole | 6 – 6.5 weeks LMP |
| Cardiac Activity | 6 – 6.5 weeks LMP |
*Above landmarks are better characterized using transvaginal US
ULTRASOUND LANDMARKS IN EARLY PREGNANCY
The Gestational Sac
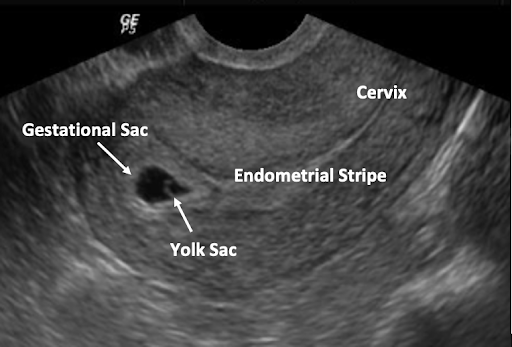
- Gestational Sac (GS) is the first evidence of pregnancy on US, as early as 4.5 weeks LMP; should always be seen by 5 weeks 5 days LMP by TVUS (Barnhart 2012).
- Although location of a pregnancy cannot definitely be diagnosed as intrauterine until a yolk sac or embryo is seen (Richardson 2015), a gestational sac still has a high likelihood of being an IUP even in the absence of certain sonographic features if there is no adnexal mass (Phillips 2020, Benson 2013).
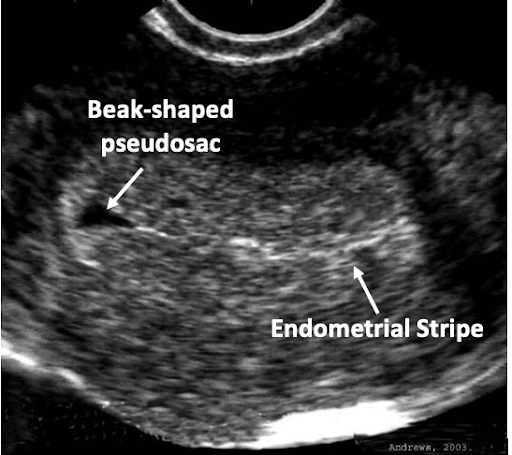
- A true gestational sac should be located in the mid to upper portion of uterus, be eccentric (not midline) to endometrial canal, be round or oval in shape, and have a double decidual (or double ring) sign, as demonstrated by the FEEDS mnemonic.
- Meeting these criteria does not completely exclude ectopic pregnancy (Fjerstad 2004)
- F – Fundal (in mid to upper uterus)
- E – Elliptical or round shape in 2 views
- E – Eccentric to the endometrial stripe
- D – Decidual reaction (surrounded by a thickened choriodecidual reaction; appears like fluffy white cloud or ring surrounding sac)
- S – Size > 4 mm (soft criteria)
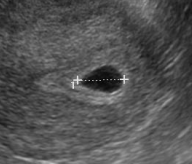
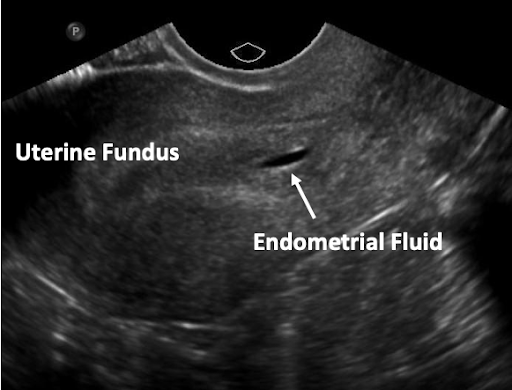
Gestational Sac vs. Pseudosac
Pseudosac
(May be associated with ectopic)
 |
 |
| Image: Fjerstad M, et al. CAPS, 2004 | Image: Dr Matt A. Morgan, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 34217 |
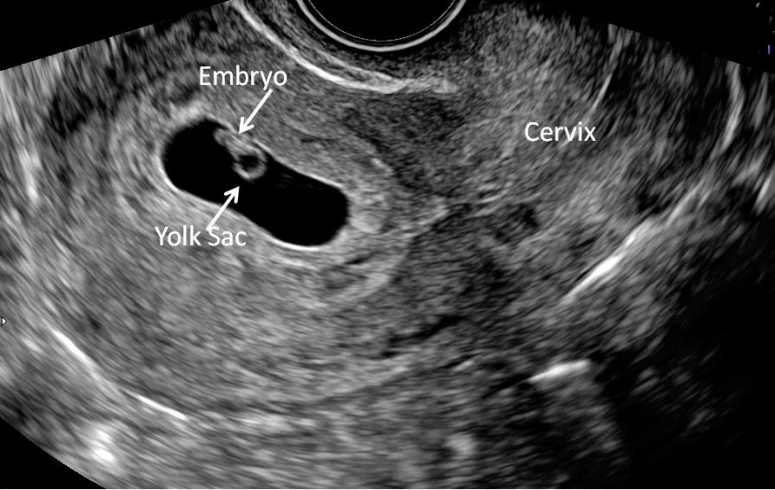
The Yolk Sac
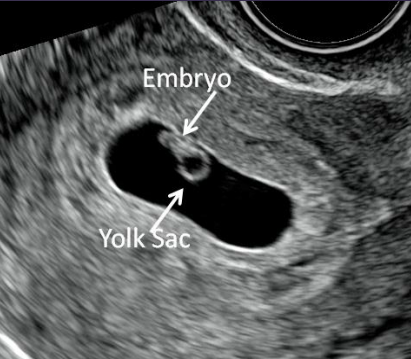
The Yolk Sac (YS) is the first single US finding that confirms an IUP. The YS is a round echoic ring with anechoic (dark) center seen within GS. It appears typically at 5 ½ weeks when the MSD is 5-10 mm. The YS should not be included when taking a measurement of the embryo. The size of the YS is not diagnostic.
The Embryo and Cardiac Activity
The embryo follows predictable development and therefore size can be used to date a pregnancy. The embryo appears at approximately 6 weeks and grows 1 mm per day until 12-14 weeks. See pregnancy dating below using embryonic and fetal measurement. Cardiac activity appears around 6 ½ weeks.
Image from AIUM 2018
Establishing Pregnancy Viability
The following data on viability evaluated patients who desired to continue their pregnancies (Doubilet 2013). If the patient does not desire to continue the pregnancy, there is no reason to delay an abortion to wait for confirmation of viability. If the patient desires to continue the pregnancy, and findings are suggestive of early pregnancy loss (see table below), repeat US in 7-10 days.
Guidelines for TVUS Diagnosis of Early Pregnancy Loss in a Patient with an IUP of Uncertain Viability
(Adapted from Doubilet 2013, ACOG 2018)
| US findings DIAGNOSTIC of EPL | US findings HIGHLY SUGGESTIVE of EPL |
|
|
EARLY PREGNANCY DATING USING ULTRASOUND
| Crown Rump Length (CRL) Measurement and Calculation of Gestational Age: | |
Calculate: GA (days) = CRL (mm) + 42 |
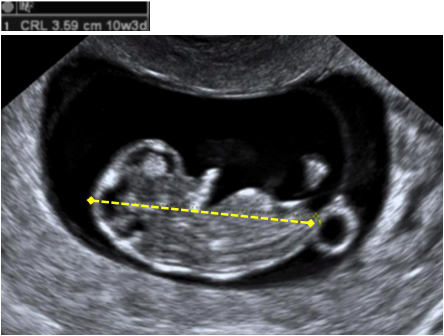
Image: AIUM 2018 |