Introduction to Osseous Tissue
The skeletal system plays a role in support, protection, and acts as a system of levers that muscle can act upon. Osseous tissue is the hard, strong tissue composed of calcium phosphate that makes up our bones. It contains nerves, blood vessels, and bone cells (osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts). Osseous tissue is divided into two types: compact bone and spongy/cancellous bone. In this chapter, we will focus on the basic structures of compact bone.
Compact bone consists of closely packed structures called osteons. Osteons consist of a central (Haversian) canal surrounded by concentric rings/layers of bone matrix called lamellae (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The central canal provides an opening for blood vessels and nerves. Sitting between the lamellae are pockets called lacunae in which the osteocytes are located. Radiating out from the lacunae are tiny channels called canaliculi that allow communication between osteocytes and access to oxygen and nutrients. The central canals are connecting to one another by perpendicular canals called perforating (Volkmann’s) canals (seen on the left side of the center panel image of Figure 1).
Figure 1: Osseous tissue under varied magnification power – scanning power (4x objective, left), low power (10x objective, center), and high power (40x objective, right).
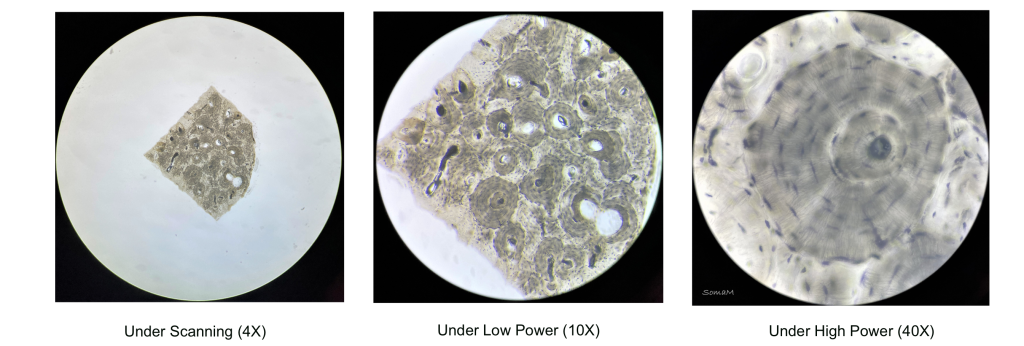
Table 1: Osseous tissue – compact bone
| Tissue Type | Osseus Tissue – Compact Bone |
|---|---|
| General Description | Organized into circular structures called osteons made up of concentric rings called lamellae with osteocytes sitting in lacunae between the rings, a central canal is found in the center of each osteon |
| Location | Outer layer of all bones |
| Function | Provides strength and protection to bones |
| Helpful Hints | Sometimes this tissue is poorly stained – the dark cells will be missing in this case and the lamellae will look transparent |
Figure 2: Osseous tissue with and without illustration overlay
Check out our YouTube video to help you understand Osseous Tissue:
YouTube Video – Osseous Tissue
We will discuss this content in more detail in The Skeletal System and The Osteon.
Chapter Illustrations By:
Soma Mukhopadhyay, Ph.D.
the functional unit in compact bone, consisting of a central (Haversian) canal surrounded by concentric rings/layers of bone matrix called lamellae
sheets or layers
A gap, cavity, or depression. Osteocytes (bone) and chondrocytes (cartilage) are found within lacunae.
mature cells in bone tissue that monitor and maintain the osseous tissue matrix
meaning "tiny canal"
running at right angles to the central canal, containing blood vessels and nerves
