The Four Major Tissue Types
The human body is made up of 11 major organ systems all working together to carry out daily necessary life functions and maintain homeostasis. These organ systems contain organs made of different tissue types working together for a common function. Tissues are groups of structurally and functionally similar cells and their extracellular environment, that carry out a predictable function in the body.
The human body is made of many different types of tissues that belong to one of four major categories, each with unique structure and function:
- Epithelial tissues – form boundaries between spaces/compartments
- Some epithelial tissues are multi-layered and provide protection and sensation
- Some epithelial tissues are single-layered and allow filtration/absorption/secretion
- Connective tissues – bind, support, protect, insulate, transport
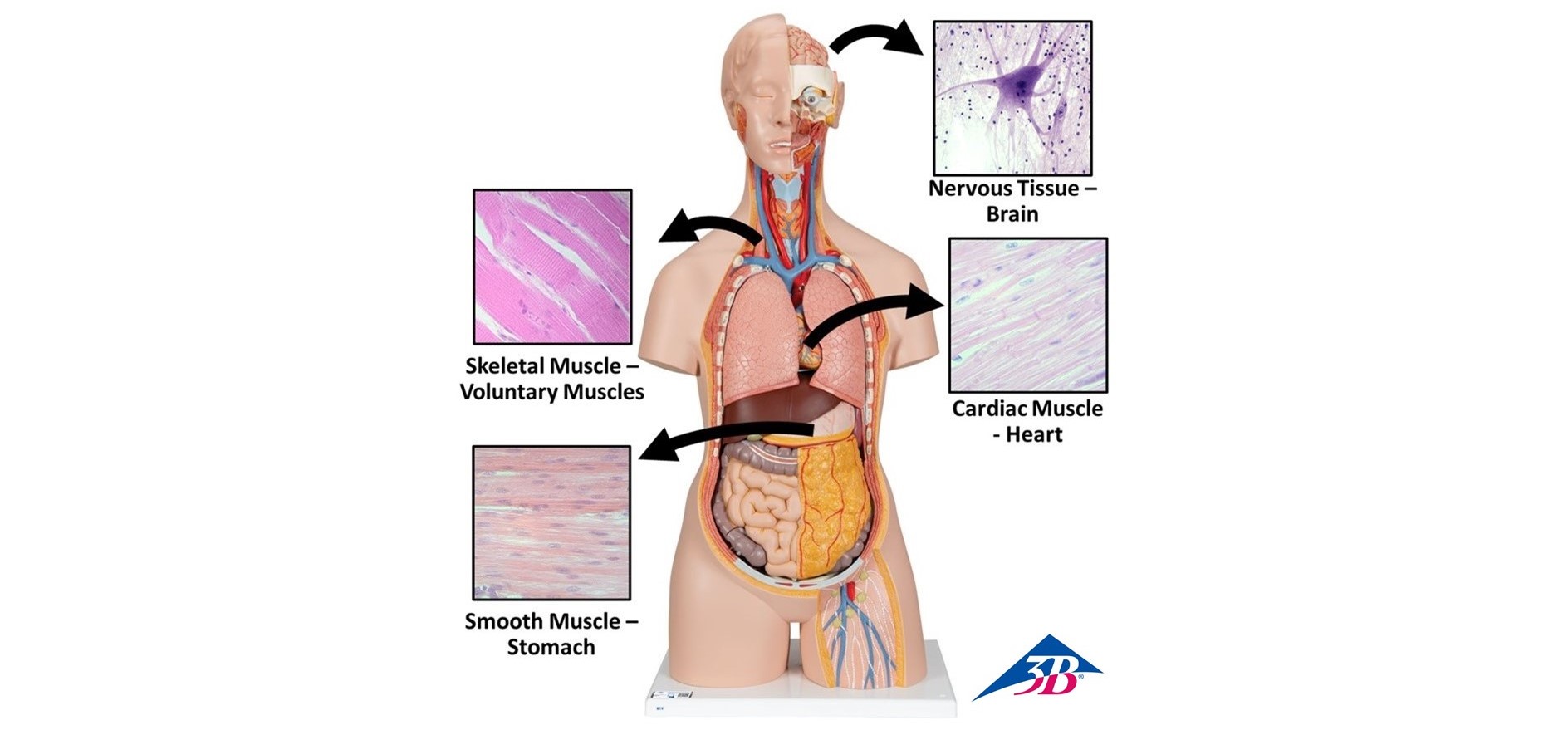
- Muscle tissue – contraction/movement
- Nervous tissue – send and receive electrical signals
Figure 1: Types and locations of epithelial tissue using a torso model
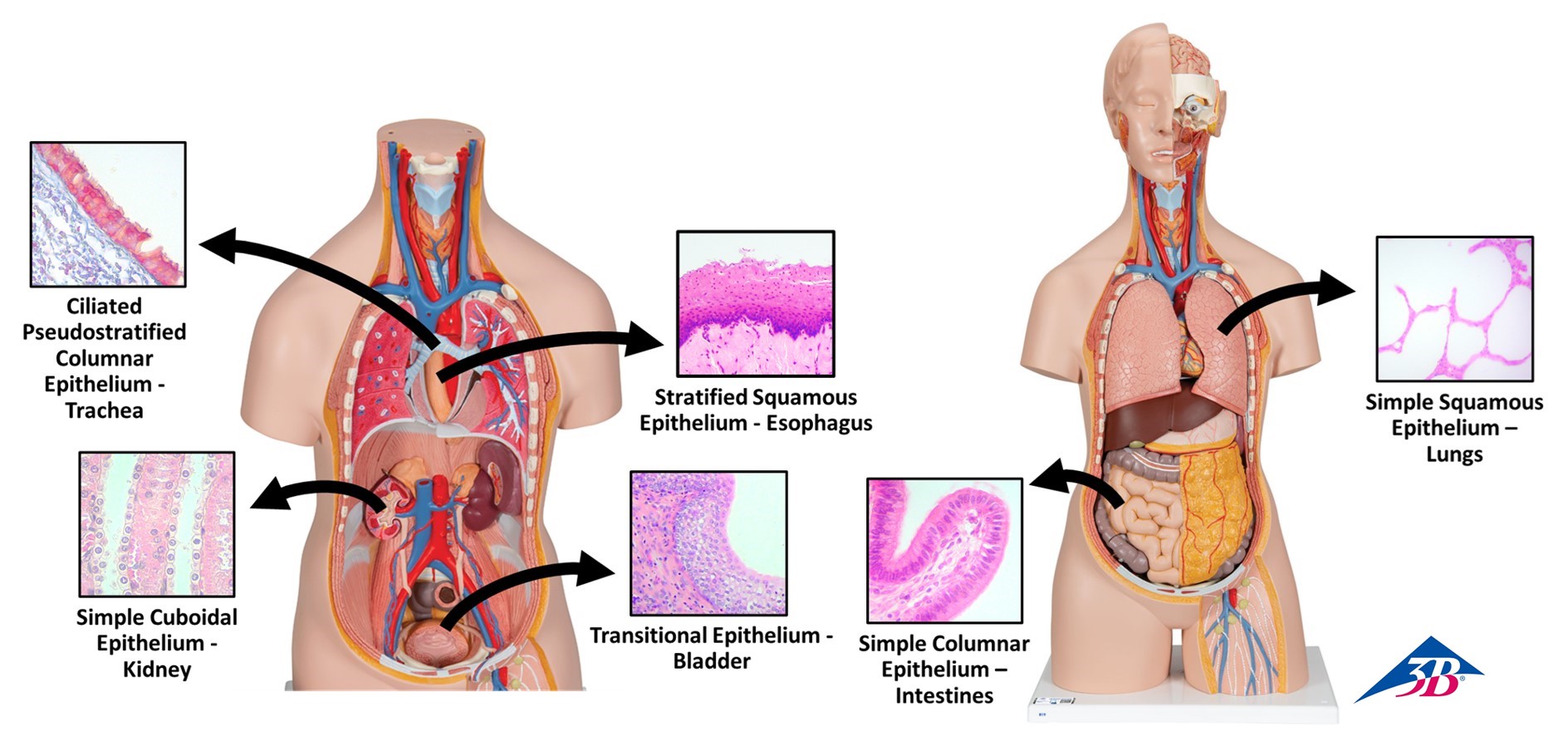
Figure 2: Types and locations of connective tissue
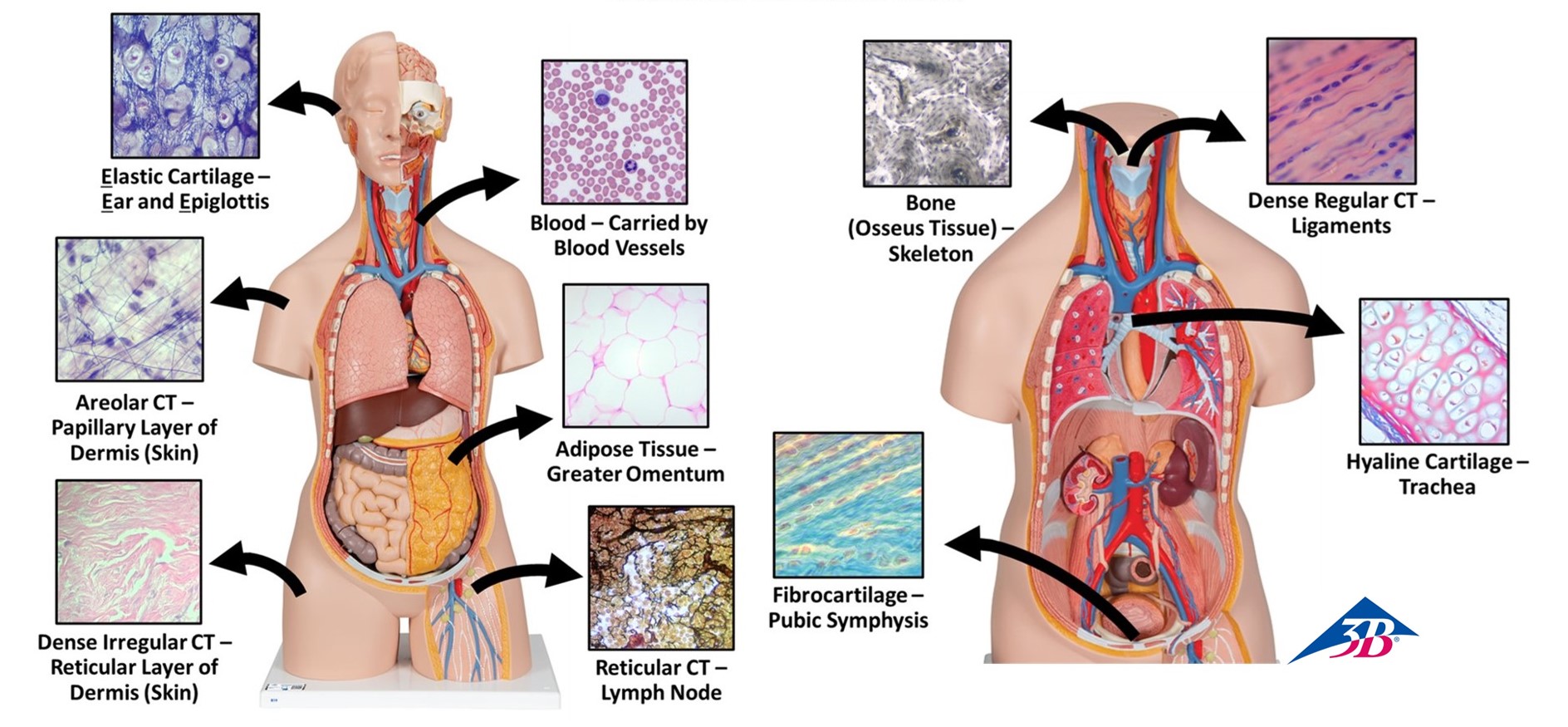
Figure 3: Types and locations of muscle and nervous tissue
As you move through the next several chapters, you will learn how to recognize and identify examples of each tissue type.
Media credits
This chapter includes images of the 3B Scientific Classic Unisex Human Torso Model – 14 Part (Item No. 1000190 [B13]).
© 3B Scientific GmbH, Germany, 2023
a dynamic (constantly adjusting) state of equilibrium
