11.7 Characteristics of Annuity Factors: A Review
Let’s review the basics of annuities:
- The number of periods counted in discounting versus compounding are different.
- The Future Value Annuity Factor (FVAF) must always be __________ than the number of compounding periods.
- The Present Value Annuity Factor (PVAF) must always be __________ than the number of discounting periods.
- FVAFs and PVAFs, unlike simple TVM factors, are not reciprocals of one another for the following reasons:
- The counting of the time periods is different for each, i.e., the timelines and “arrows’ directions” are different, therefore so are the simple factors’ respective exponents!
- The annuity factors are themselves the result of an additive (aggregating) process for which reciprocals do not apply, e.g., 1 ÷ (1 + 2 + 3) ≠ 1/1 + ½ + 1/3. The reciprocal of a sum is not equal to the sum of reciprocals.
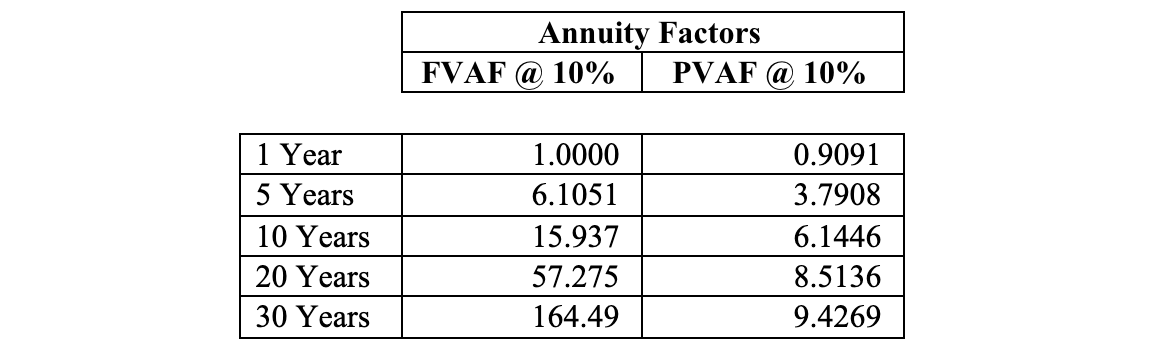
The answers to the fill-ins above are:
- The FVAF must always be – greater – than the number of compounding periods.
- The PVAF must always be – less – than the number of discounting periods.
Notes:
- Over 30 years, an investor who has invested $100 per year at 10% will have put down $100 × 30 = $3,000 in nominal terms. The FV of the $100 annuity at 10% in comparison will be $100 × 164.49 = $16,449
- Notice how quickly both the present and future value annuity factors increase. That is because we are constantly adding additional cash flows each year. That is also why the PVAFs increase, in contrast to the simple PV factors, which, of course, may only decrease – as per our three commandments – as time increases.
Key:
PVAF = Present Value Annuity Factor
FVAF = Future Value Annuity Factor
