2.4 Sample Bookkeeping Entries
Here are some examples of simple bookkeeping (or “journal” or “ledger”) entries, exemplifying double-entry bookkeeping standards. Keep in mind that assets are debit balance accounts, while liabilities and equity are credit balance accounts. Debits must always equal credits. (All the numbers below are in thousands of dollars.)
- Let’s say that a company buys inventory for $1,000 in cash. What are the correct bookkeeping entries?
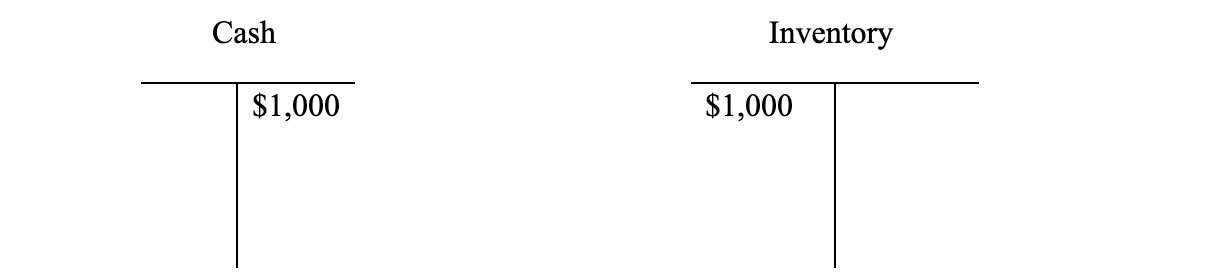 You will note that cash goes down (credit) and inventory goes up (debit). You will note that the basic accounting equation (A = L + E) remains unchanged.
You will note that cash goes down (credit) and inventory goes up (debit). You will note that the basic accounting equation (A = L + E) remains unchanged. - What happens when a company borrows money by issuing long-term debt for $5,000?
 First, debt increases (credit) and so too will cash (debit). You will note that both sides of the the basic accounting equation increase.
First, debt increases (credit) and so too will cash (debit). You will note that both sides of the the basic accounting equation increase. - What if the company borrows $7,500 in order to buy back some of its stock?
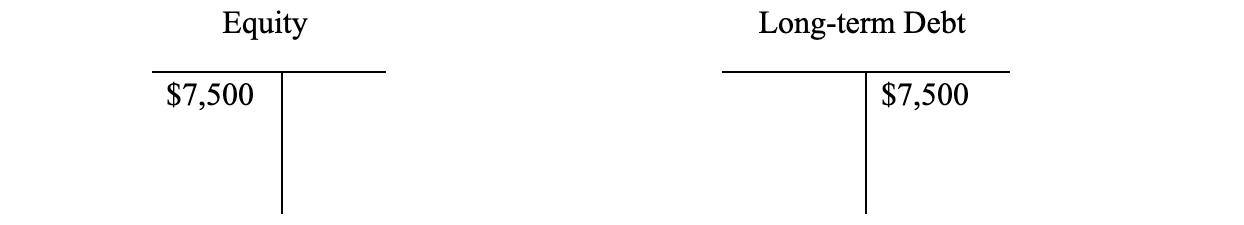 Debt increases (credit) and equity goes down (debit). The purchased equity becomes what is called “Treasury Stock,” which is a contra-account and thus a debit balance account. The equity may be reissued again in the future, should the company choose to do so. Another example of a contra-account would be “Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Receivables,” which would be a credit balance account versus accounts receivables.
Debt increases (credit) and equity goes down (debit). The purchased equity becomes what is called “Treasury Stock,” which is a contra-account and thus a debit balance account. The equity may be reissued again in the future, should the company choose to do so. Another example of a contra-account would be “Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Receivables,” which would be a credit balance account versus accounts receivables. - What happens when the company buys $500 in inventory on credit terms?
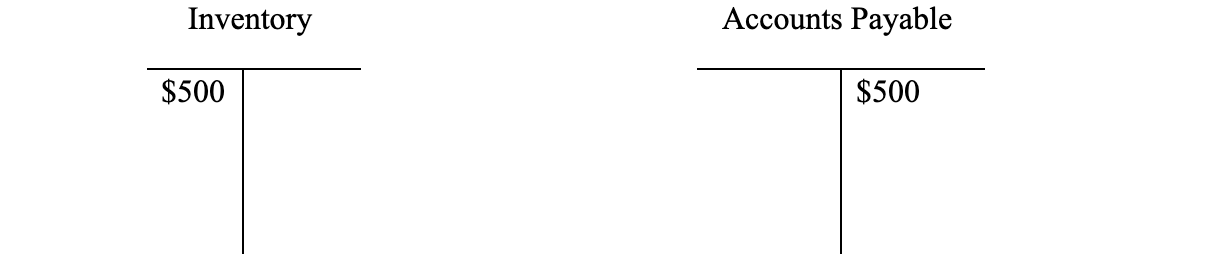 Inventory rises (debit) and payables also increase (credit).
Inventory rises (debit) and payables also increase (credit).
